Define these Vocab.
Vocabulary:
1) Town: the central part of a neighborhood, with its business or shopping area
2)Charter: a written grant by a country's legislative or sovereign power, by which an institution such as a company, college, or city is created and its rights and privileges defined.
3)Guild: a medieval association of craftsmen or merchants, often having considerable power.
4)Guild Hall: building used as the meeting place of a guild or corporation.
5)Journeyman: a trained worker who is employed by someone else.
6)Apprentice: a person who is learning a trade from a skilled employer, having agreed to work for a fixed period at low wages.
7)Merchant: a person or company involved in wholesale trade, especially one dealing with foreign countries or supplying merchandise to a particular trade.
8)Barter: exchange (goods or services) for other goods or services without using money
9)Carpenter: a person who makes and repairs wooden objects and structures.
10)Cobbler: a person who mends shoes as a jggob.
11)Glover: a maker of gloves.
12)Blacksmith: a person who makes and repairs things in iron by hand
13)Tinker: a person who travels from place to place mending metal utensils as a way of making a living.
14)Potter: British term for putter
15)Copper: a red-brown metal, the chemical element of atomic number 29.
16)Wheel right(wheeler): a vehicle having a specified number of wheels.
17)Tanner: a person who tans animal hides, especially to earn a living.
18)Weaver: a person who weaves fabric.
19)Baker: a person who makes bread and cakes, especially commercially.
20)Butcher: a person whose trade is cutting up and selling meat in a shop.
21)Inn: a person whose trade is cutting up and selling meat in a shop
22)Tavern: an establishment for the sale of beer and other drinks to be consumed on the premises, sometimes also serving food.
23)Barber: a person who cuts hair, especially men's, and shaves or trims beards as an occupation.
24)Fuller: a person who fulls cloth.
25)Miller: a person who owns or works in a grain mill.
26)Brewer: To make (ale or beer) from malt and hops by infusion, boiling, and fermentation.
27)Stable: not likely to change or fail; firmly established.
28)Craft Guild: an association of workers of the same trade for mutual benefit.
29)Merchant Guild : control the practice of their craft in a particular town. The earliest types of guild were formed as confraternities of tradesmen.
30)Wattle and Daub: Watter: a material for making fences, walls, etc., consisting of rods or stakes interlaced with twigs or branches. Daub: coat or smear (a surface) with a thick or sticky substance in a carelessly rough or liberal way.
Thursday, May 5, 2016
Friday, April 29, 2016
Questions/Answers On "Castle"
1. Who were the people dependent upon? The people were dependent upon a lord.
2. Where did they choose to build? And why? They choose to build on a rock, because they thought it would be easily to escape.
3. What was the first ring of the castle called? The first ring of the castle was called "Inner Curtain."
4. How long will the walls be on the outer curtain? On the outer curtain it will be 300 ft long.
5. How thick was the inner curtain? How high? The inner curtain was 35 ft high with 54 high tower.
6. Make a sketch. My sketch's link) COPY AND PASTE THE LINK AND YOU WILL SEE THE PICTURE
https://picasaweb.google.com/104792482958602344175/6280265118799508225#6280265121250085442
7. What's the center of the inner ward? In the center of the inner ward they have the living quarters for yourself and Lady Cathrine.
8. How many entrances in the town hall? How are they protected?
There are 3 entrances in the town hall.
9. Why did people move to towns? People moved to towns because they felt it was more safe there.
10. What were the walls filled with? The walls are filled with rubble materials and scaffolding supported by put gloves.
11. How are the windows designed, starting from the bottom to the top of the towers? The windows near the bottom of walls must be small enough so that enemy solider can be harmful to all the windows will be protected by iron grids, closed by wooden shutters inside.
12. What are the crenelations used for? The crenelations were used for having a margin or contour with shallow.
13. Why are the gate houses not lined up from the inner to the outer ward? The gate houses are not lined up from the inner to outer ward because you can shoot from two walls.
14. How are the towers level divided? The towers are divided by lowest one, the basement level.
15. What defenses are in gate houses? The defenses in a gate house is most valuable, lowed to block the enterce, insert wooden door.
16. What are the building made from? The buildings was made of mud and wax.
17. What lived on the bottom floor of the barracks? The top? On the top was a slate roof and down in the bottom was where the soldiers were.
18. What is a garderobe? A garderobe is a lavatory in a medieval building.
19. Why were nicer rooms higher in the towns? There was nicer rooms in the towns because it was meant for special guests, it was also a safer place.
20. How thick were the walls? The walls were about 8 ft thick.
21. What was used to heat the rooms? To heat the rooms they used fire.
22. How many rooms were in a tower? In a tower there were
23. What was the most important room in a castle? In a castle the most important room was
24. How did peasants live? Peasants lived in shacks (huts).
25. What was the main material that was used to build medieval homes? The main material that was used to build medieval homes was wattle and daub.
26. What is a wattle? What is a daub? A wattle is a wooden lattices sticks. A daub is a mixture of mud.
27. Why did people settle in towns? People settled in towns because they had more profit selling cows and sheep.
28. What was the best location in a town? The best location in a town was in a house.
29. What were the floors(bottom) made of? The bottom of the floor was made of ground dirt.
30. What were the windows covered with? The windows were covered with sheepskin.
31. What was the main source of heat and light? The main source of heat and light was fire.
32.Why would no one want to be live behind the butcher shop? No one wanted to live behind the butcher shop because the enemies lived near there.
33. What does a barber do? A barbers jobs is to
34. Are the sewers? No, they did not have sewers.
35, Are the toilets? Yes, there are toilets.
36. Where does the waste go? The waste goes to a tunnel leading to the ground
1. Who were the people dependent upon? The people were dependent upon a lord.
2. Where did they choose to build? And why? They choose to build on a rock, because they thought it would be easily to escape.
3. What was the first ring of the castle called? The first ring of the castle was called "Inner Curtain."
4. How long will the walls be on the outer curtain? On the outer curtain it will be 300 ft long.
5. How thick was the inner curtain? How high? The inner curtain was 35 ft high with 54 high tower.
6. Make a sketch. My sketch's link) COPY AND PASTE THE LINK AND YOU WILL SEE THE PICTURE
https://picasaweb.google.com/104792482958602344175/6280265118799508225#6280265121250085442
7. What's the center of the inner ward? In the center of the inner ward they have the living quarters for yourself and Lady Cathrine.
8. How many entrances in the town hall? How are they protected?
There are 3 entrances in the town hall.
9. Why did people move to towns? People moved to towns because they felt it was more safe there.
10. What were the walls filled with? The walls are filled with rubble materials and scaffolding supported by put gloves.
11. How are the windows designed, starting from the bottom to the top of the towers? The windows near the bottom of walls must be small enough so that enemy solider can be harmful to all the windows will be protected by iron grids, closed by wooden shutters inside.
12. What are the crenelations used for? The crenelations were used for having a margin or contour with shallow.
13. Why are the gate houses not lined up from the inner to the outer ward? The gate houses are not lined up from the inner to outer ward because you can shoot from two walls.
14. How are the towers level divided? The towers are divided by lowest one, the basement level.
15. What defenses are in gate houses? The defenses in a gate house is most valuable, lowed to block the enterce, insert wooden door.
16. What are the building made from? The buildings was made of mud and wax.
17. What lived on the bottom floor of the barracks? The top? On the top was a slate roof and down in the bottom was where the soldiers were.
18. What is a garderobe? A garderobe is a lavatory in a medieval building.
19. Why were nicer rooms higher in the towns? There was nicer rooms in the towns because it was meant for special guests, it was also a safer place.
20. How thick were the walls? The walls were about 8 ft thick.
21. What was used to heat the rooms? To heat the rooms they used fire.
22. How many rooms were in a tower? In a tower there were
23. What was the most important room in a castle? In a castle the most important room was
24. How did peasants live? Peasants lived in shacks (huts).
25. What was the main material that was used to build medieval homes? The main material that was used to build medieval homes was wattle and daub.
26. What is a wattle? What is a daub? A wattle is a wooden lattices sticks. A daub is a mixture of mud.
27. Why did people settle in towns? People settled in towns because they had more profit selling cows and sheep.
28. What was the best location in a town? The best location in a town was in a house.
29. What were the floors(bottom) made of? The bottom of the floor was made of ground dirt.
30. What were the windows covered with? The windows were covered with sheepskin.
31. What was the main source of heat and light? The main source of heat and light was fire.
32.Why would no one want to be live behind the butcher shop? No one wanted to live behind the butcher shop because the enemies lived near there.
33. What does a barber do? A barbers jobs is to
34. Are the sewers? No, they did not have sewers.
35, Are the toilets? Yes, there are toilets.
36. Where does the waste go? The waste goes to a tunnel leading to the ground
Monday, April 25, 2016
Our assignment is to define vocabulary words for our next project, which is about fiefdom.
3rd Trimester Fiefdom Vocabulary Words:
Fiefdom: A fief.
Feudalism: The dominant social system in medieval Europe.
Monarch: A sovereign head of state.
Lord: Someone or something having power, authority, or influence; a master or ruler
Vassal: Someone or something having power, authority, or influence; a master or ruler
Knight: A man who served his sovereign or lord as a mounted soldier in armor.
Peasant: A poor farmer of low social status who owns or rents a small piece of land for cultivation
Commoner: An ordinary person, without rank or title.
Serf: An agricultural laborer bound under the feudal system to work on his lord's estate.
Tradesman: A person engaged in trading or a trade, typically on a relatively small scale.
Merchant: A person or company involved in wholesale trade
Castle: A large building or group of buildings fortified against attack with thick walls, battlements, towers, and in many cases a moat.
Moat: A deep, wide ditch surrounding a castle
Guild: A medieval association of craftsmen or merchants, often having considerable power.
Abbey: The building or buildings occupied by a community of monks or nuns.
High middle ages: The period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries
100 years war: A war between France and England that lasted from middle of the fourteenth century to the middle fifteen.
Black death: An epidemic outbreak of bubonic plague in Europe around 1348 that killed between one third of the population in less than five years.
3rd Trimester Fiefdom Vocabulary Words:
Fiefdom: A fief.
Feudalism: The dominant social system in medieval Europe.
Monarch: A sovereign head of state.
Lord: Someone or something having power, authority, or influence; a master or ruler
Vassal: Someone or something having power, authority, or influence; a master or ruler
Knight: A man who served his sovereign or lord as a mounted soldier in armor.
Peasant: A poor farmer of low social status who owns or rents a small piece of land for cultivation
Commoner: An ordinary person, without rank or title.
Serf: An agricultural laborer bound under the feudal system to work on his lord's estate.
Tradesman: A person engaged in trading or a trade, typically on a relatively small scale.
Merchant: A person or company involved in wholesale trade
Castle: A large building or group of buildings fortified against attack with thick walls, battlements, towers, and in many cases a moat.
Moat: A deep, wide ditch surrounding a castle
Guild: A medieval association of craftsmen or merchants, often having considerable power.
Abbey: The building or buildings occupied by a community of monks or nuns.
High middle ages: The period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries
100 years war: A war between France and England that lasted from middle of the fourteenth century to the middle fifteen.
Black death: An epidemic outbreak of bubonic plague in Europe around 1348 that killed between one third of the population in less than five years.
Sunday, April 24, 2016
Extra Credit: Salah Ad Din
Question:
Who was Salah Ad Din? What did he gift Richard I when he was sick during the King Crusade?
ANSWER:
Salah was a Muslim. Salah Ad Din was the first sultan of Egypt and Syria and the founder of the Ayyubid Dynasty. He was also known as Saladin. In fact, he was called Saladin. Although, during the Crusades, Saladin was Richard's I enemy, he negotiated a peace treaty with him and the two kings developed respect, even friendship. The gift that Salah Ad Din gave to Richard I was respect and a peace treaty.
.
Question:
Who was Salah Ad Din? What did he gift Richard I when he was sick during the King Crusade?
ANSWER:
Salah was a Muslim. Salah Ad Din was the first sultan of Egypt and Syria and the founder of the Ayyubid Dynasty. He was also known as Saladin. In fact, he was called Saladin. Although, during the Crusades, Saladin was Richard's I enemy, he negotiated a peace treaty with him and the two kings developed respect, even friendship. The gift that Salah Ad Din gave to Richard I was respect and a peace treaty.
.
Tuesday, April 19, 2016
Meal Assignment:
* Fried Fish
* White Rice
* Boiled Vegetables
* Oat Cake
* Cider
Recipes/Ingredients:
Basic Oatcakes:
* 1 LB whole meal flour
* 8 Oz oatmeal
(Mix all the ingredients together in a large bowl until you have a fairly wet dough. Cover with a damp cloth and leave out of the sun for about 30 minutes, by which time the dough will have stiffened. Flour your hands, break off walnut sized pieces of dough, and shape them into flat cakes. Get your griddle good and hot, or they will cook slowly and turn into hockey pucks! Cook the cakes quickly for about 30 seconds each side. Serve hot or cold, with just about anything.)
Fried Fish:
* 3 fish fillets
* 1 bar of butter
* Bread crumbs
* Salt
Add butter to pan. In a plate add bread crumbs to fish fillet and put it in pan. Once it's on the pan add salt.
Boiled Vegetables:
* 3-4 carrots
* 1 pinch of salt
* 1 bunch of broccoli
* 1/2 a cup of water
(Choose your vegetables and add them in you pot with water. Boil them until it is ready. Add salt to have taste.)
White Rice:
* Rice
* Salt
* Water
Add rice to a boiling pot with water. Boil it until it is cooked. Later on, add salt to taste.
Pictures of Cooking and Meals:
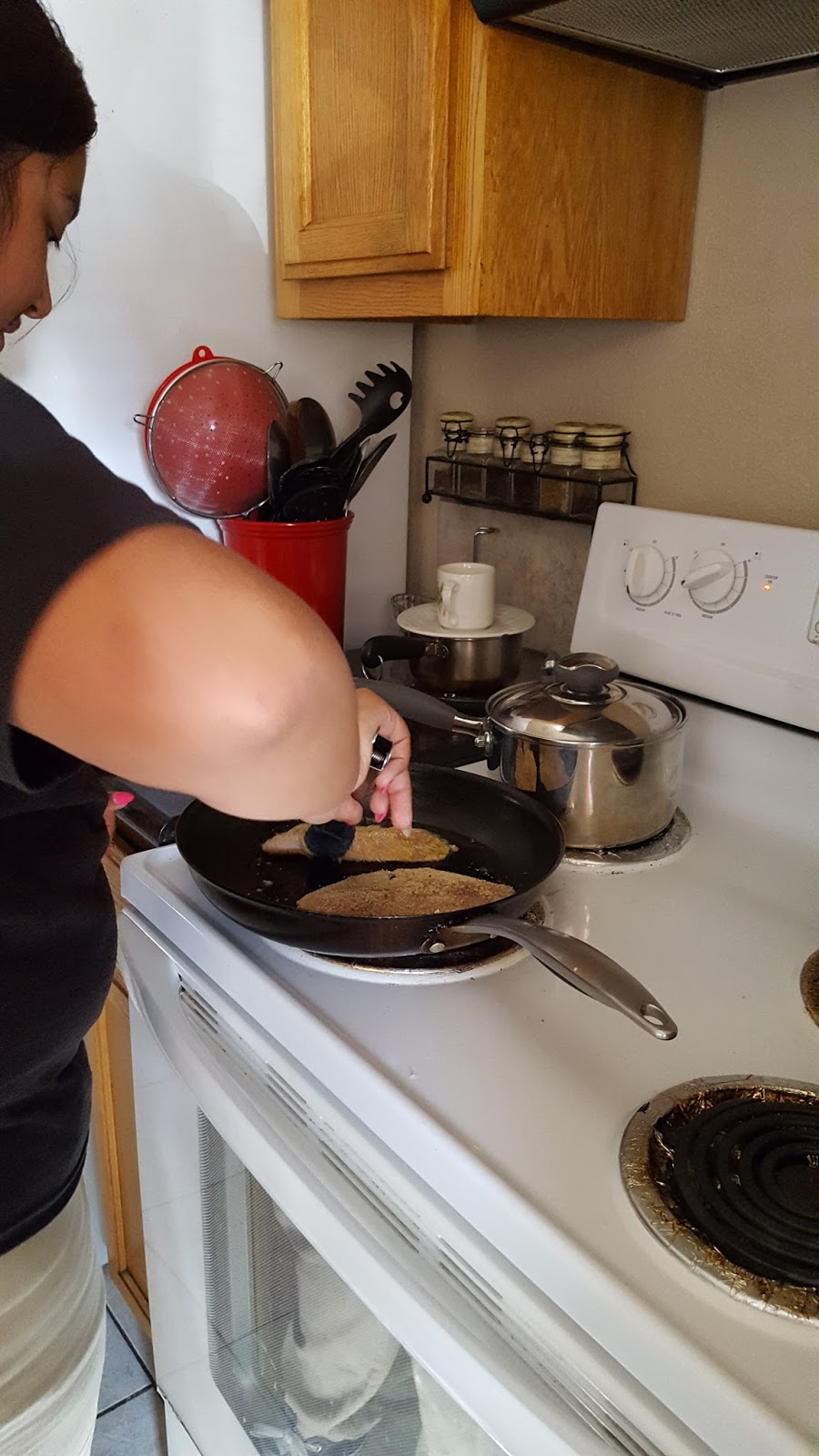
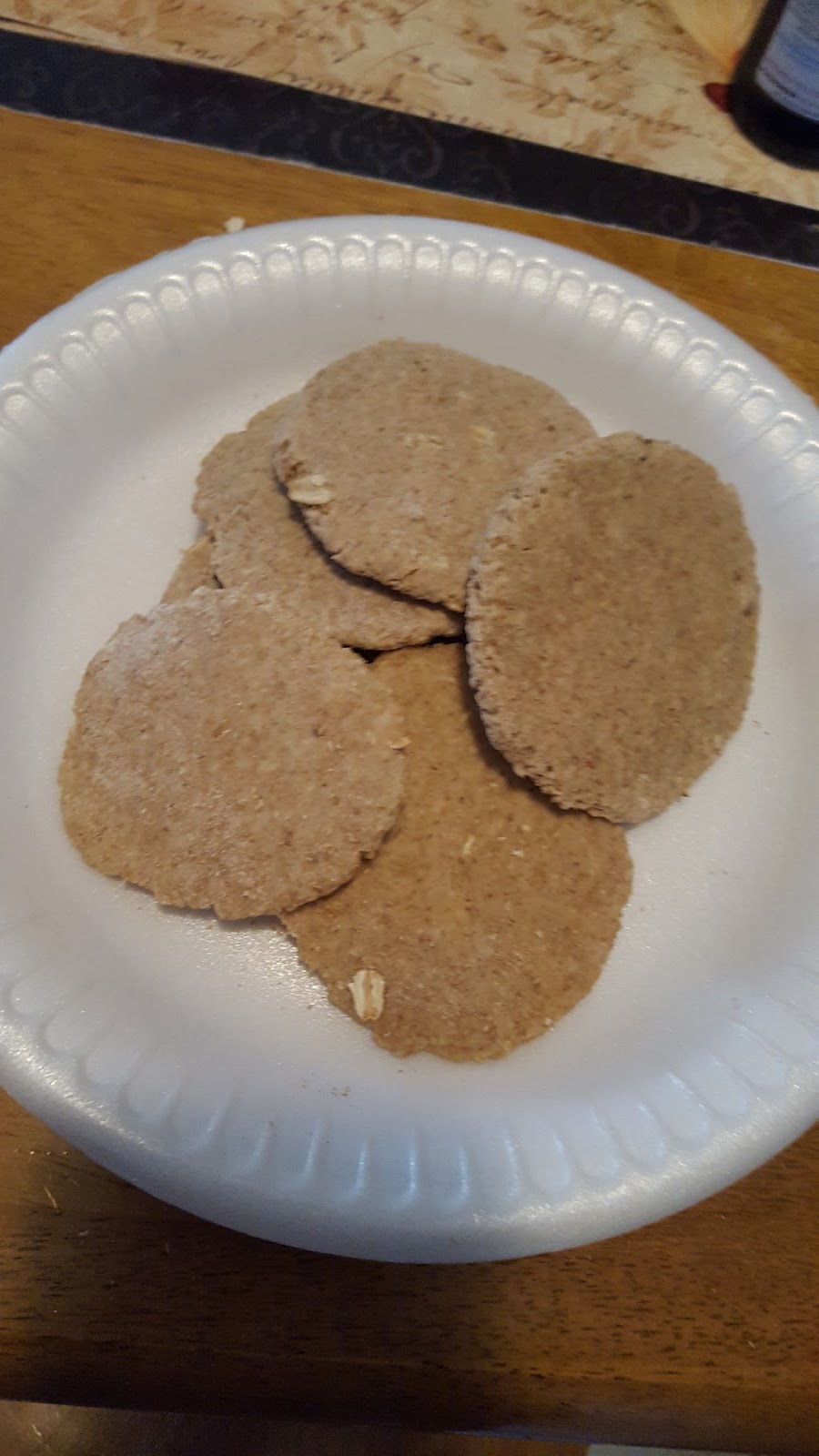






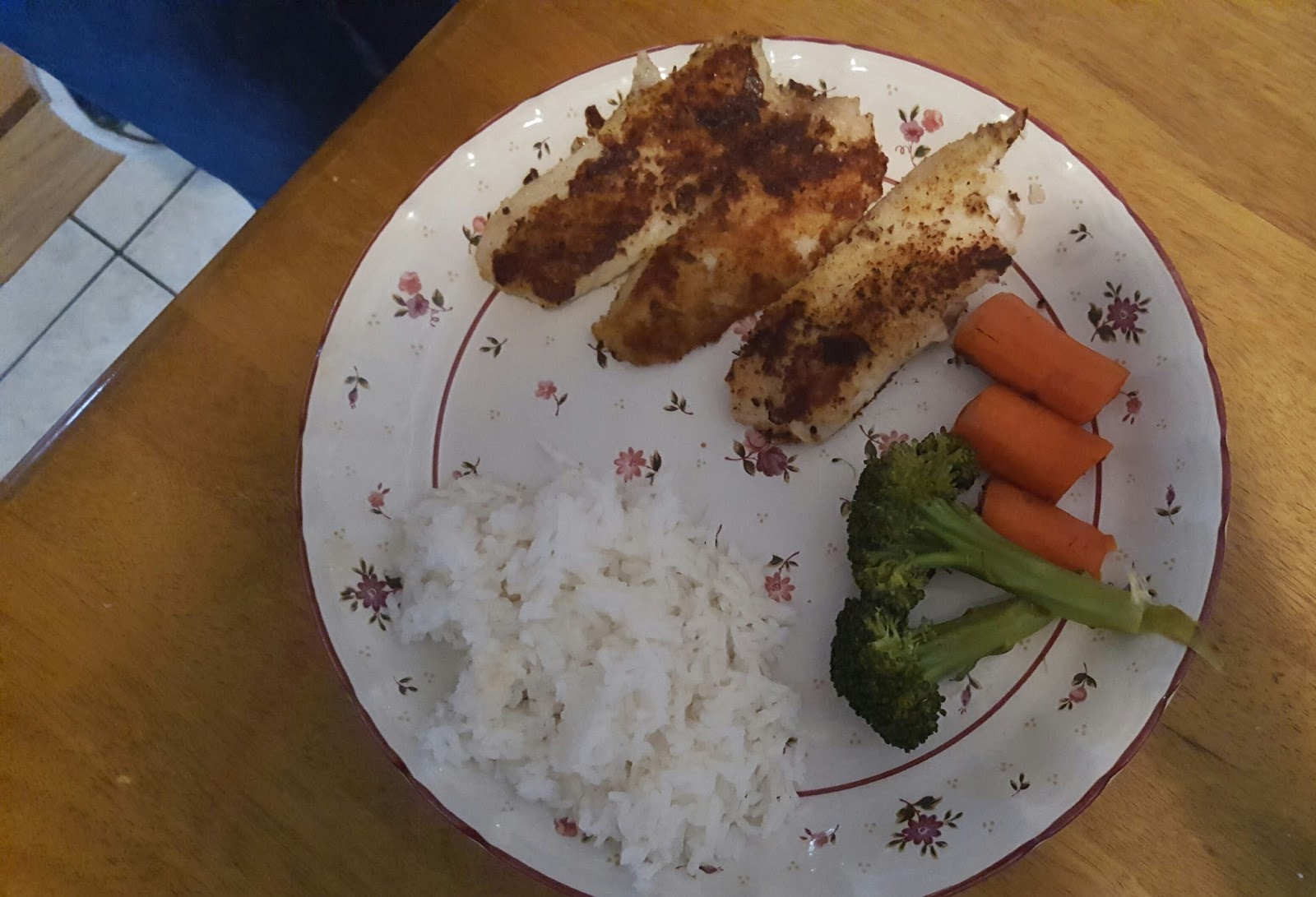
Cites For Meal Project:
http://www.medieval-recipes.com/
http://thevikingworld.pbworks.com/w/page/4842629/Traditional%20Viking%20Foods
* Fried Fish
* White Rice
* Boiled Vegetables
* Oat Cake
* Cider
Recipes/Ingredients:
Basic Oatcakes:
* 1 LB whole meal flour
* 8 Oz oatmeal
(Mix all the ingredients together in a large bowl until you have a fairly wet dough. Cover with a damp cloth and leave out of the sun for about 30 minutes, by which time the dough will have stiffened. Flour your hands, break off walnut sized pieces of dough, and shape them into flat cakes. Get your griddle good and hot, or they will cook slowly and turn into hockey pucks! Cook the cakes quickly for about 30 seconds each side. Serve hot or cold, with just about anything.)
Fried Fish:
* 3 fish fillets
* 1 bar of butter
* Bread crumbs
* Salt
Add butter to pan. In a plate add bread crumbs to fish fillet and put it in pan. Once it's on the pan add salt.
Boiled Vegetables:
* 3-4 carrots
* 1 pinch of salt
* 1 bunch of broccoli
* 1/2 a cup of water
(Choose your vegetables and add them in you pot with water. Boil them until it is ready. Add salt to have taste.)
White Rice:
* Rice
* Salt
* Water
Add rice to a boiling pot with water. Boil it until it is cooked. Later on, add salt to taste.
Pictures of Cooking and Meals:






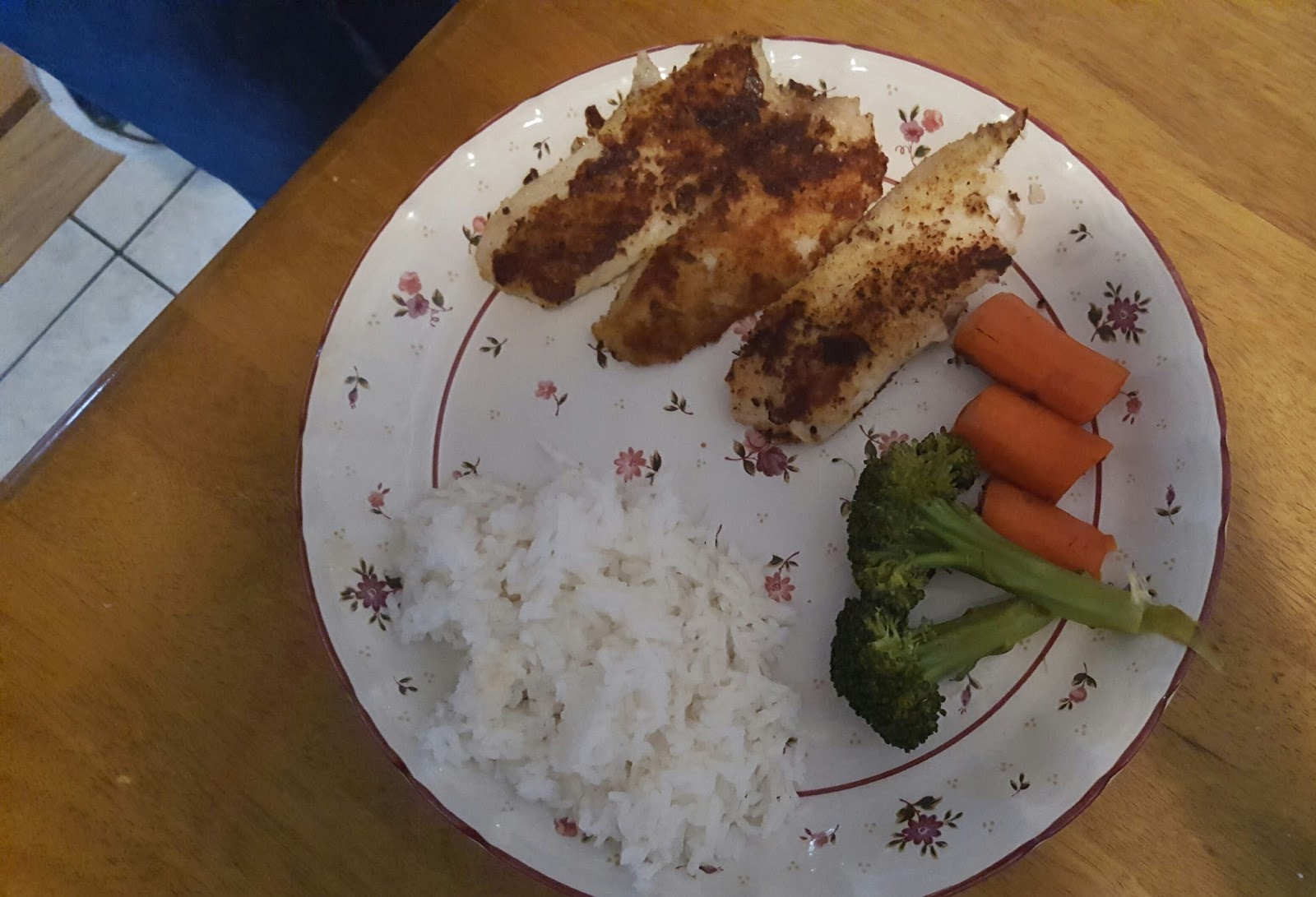
Cites For Meal Project:
http://www.medieval-recipes.com/
http://thevikingworld.pbworks.com/w/page/4842629/Traditional%20Viking%20Foods
Monday, April 18, 2016
Saturday, April 9, 2016
Compare + Contrast Magna Carta & U.S Constitution
Similarities Between Magna Carta & U.S Constitution:
* Magna Carta involves the freedom of the church.
* In Constitution, freedom of religion is guaranteed.
* In Magna Cart, only the Parliament could levy taxes, not king.
* The U.S , doesn't have a Parliament, the Congress levies taxes, not president.
* In Magna Carta, it is guaranteed that everyone has the right to fair trail.
* In U.S., the three branches of government are the parallel to the parliament.
*In both documents, both include the right of fair fines.
* They both state that the fine is associated with the degree of offense.
* They both develop to become the law of the land and counties to be used this day.
Differences Between Magna Carta & U.S Constitution:
* were created at different time periods.
* were created at different places.
* The constitution didn't do anything for slaves, but everyone else was protected by it, on the other side Magna Carta was not really written to apply to everyone in society that time.
* Magna Carta only talks about things like trails and crimes, it does not really give personal freedoms that are important to us, but U.S Constitution does.
* The Bill of Rights was to develop to protect the citizens of American colonies from the British, but Magna Carta was not.
* The Magna Carta was written in Feudal England, the U.S Constitution in post Revolutionary War Enlightenment America.
Similarities Between Magna Carta & U.S Constitution:
* Magna Carta involves the freedom of the church.
* In Constitution, freedom of religion is guaranteed.
* In Magna Cart, only the Parliament could levy taxes, not king.
* The U.S , doesn't have a Parliament, the Congress levies taxes, not president.
* In Magna Carta, it is guaranteed that everyone has the right to fair trail.
* In U.S., the three branches of government are the parallel to the parliament.
*In both documents, both include the right of fair fines.
* They both state that the fine is associated with the degree of offense.
* They both develop to become the law of the land and counties to be used this day.
Differences Between Magna Carta & U.S Constitution:
* were created at different time periods.
* were created at different places.
* The constitution didn't do anything for slaves, but everyone else was protected by it, on the other side Magna Carta was not really written to apply to everyone in society that time.
* Magna Carta only talks about things like trails and crimes, it does not really give personal freedoms that are important to us, but U.S Constitution does.
* The Bill of Rights was to develop to protect the citizens of American colonies from the British, but Magna Carta was not.
* The Magna Carta was written in Feudal England, the U.S Constitution in post Revolutionary War Enlightenment America.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)